Beautiful legs – are they real? The best exercises and techniques for strengthening
- Advertisement -
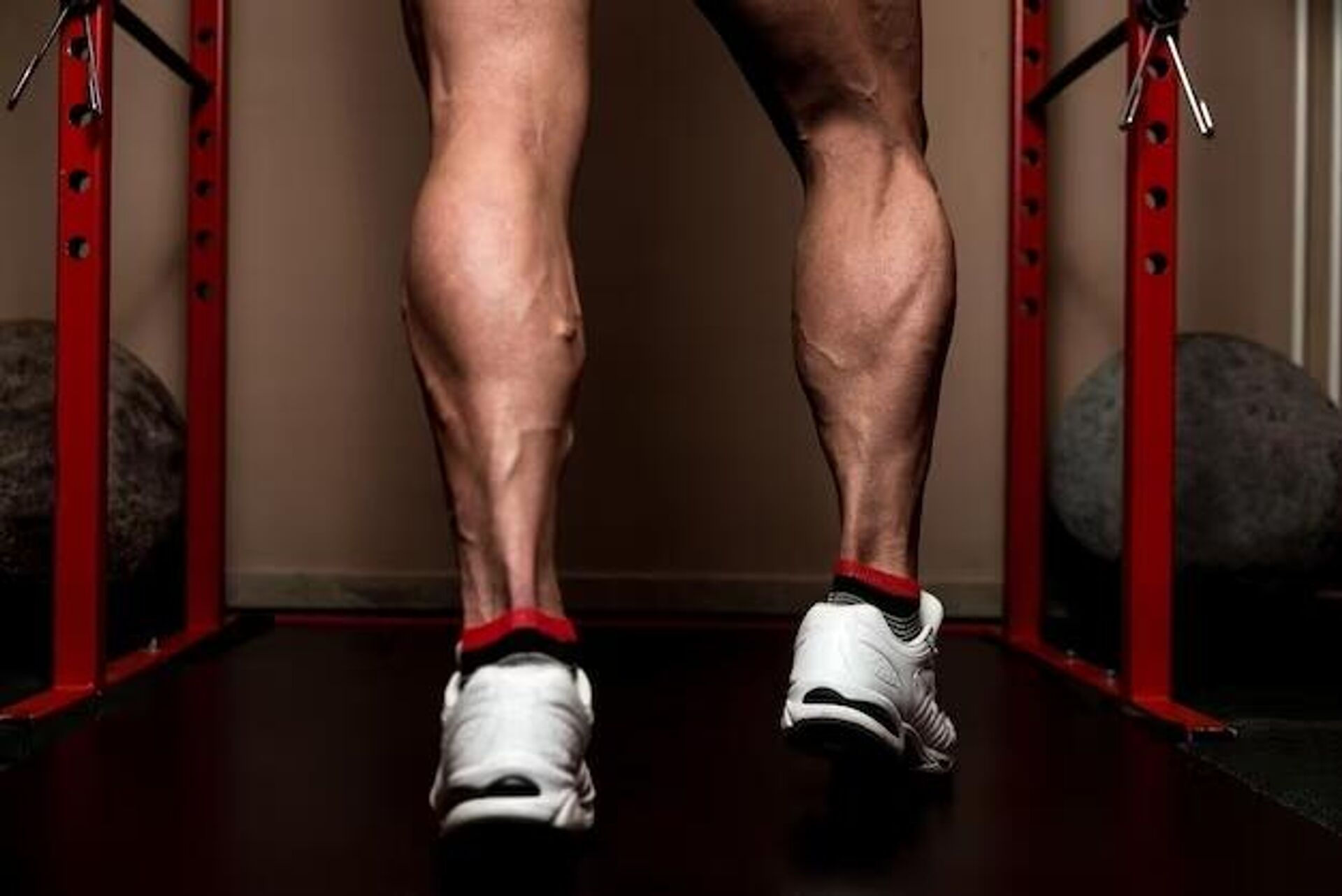
- calf muscles
- anatomy
- species and groups
- What are the functions
- Causes of pain in the leg area
- Strengthening the leg muscles
- exercises
calf muscles
anatomy
- Advertisement -

species and groups
-
–
frontal tibia
-
–
long extensor of the fingers
-
–
long extensor of the thumb.
-
–
Three heads.
-
–
plantar.
-
–
popliteal.
-
–
posterior, tepal;
-
–
Flex the long finger
-
–
Long flexed thumb.
What are the functions
|
muscle group |
muscle |
mission |
|
Before |
tibialis anterior |
Extends, rounds and feeds the foot |
|
long extensor finger |
It extends the toes and penetrates the foot |
|
|
long thumb extensor |
Extends the big toe and foot |
|
|
sidebar |
Long and short peroneal muscles |
They pierce the foot and bend it. Short is involved in foot abduction |
|
back (surface layer) |
Triceps muscle in the leg |
Flexes the foot. The calf muscle is also involved in flexing the leg at the knee joint. |
|
plantar muscle |
Tighten the knee joint capsule while flexing and rotating the lower leg |
|
|
back (deep layer) |
Long toe flexor |
Flexes the fingers and toes |
|
posterior tibial |
It flexes and overshadows the foot. He presses his fingers on the ground in a stable body position |
|
|
Long thumb flexor |
The big toe flexes and replaces the foot |
Causes of pain in the leg area
-
–
Meniscus injury
-
–
Fractures of the bones of the lower leg or ankle joint.
-
–
Muscle tear.
-
–
contraction (“blockage”) of the muscle;
-
–
patellar condyle (jumper’s knee);
-
–
torn or torn ligaments/tendons;
-
–
Achilles tendon injury, etc.
-
1
Decreased concentration of salts in the blood due to taking diuretics.
-
2
Uncontrolled use of statins that cause destruction/deformation of muscle tissue.
-
3
Vein thrombosis, varicose veins.
-
four
Atherosclerosis in the vessels of the legs.
-
five
Various deformities and damage to nerve fibers caused by diabetes, smoking and alcohol abuse.
-
6
Muscle fatigue, compression of nerve endings caused by a lack of physical activity.
-
7
Infectious lesions of muscle tissue.
-
8
Inflammation of the tuberous surface of the tibia.
-
nine
Tumor or bone tumor in the lower leg/femur.
-
10
Bone and soft tissue infections.

Strengthening the leg muscles
-
1
Each workout should begin with a warm-up aimed at warming up the joints, muscles and ligaments of the legs.
-
2
All movements should be smooth. It is important to avoid jerking and sudden movements so as not to damage muscle fibers and tendons.
-
3
After the exercise, you need to stretch. Stretching helps relax the muscles and speed up the healing process.

exercises
-
1
rises on socks. On exhalation, raise the toes as high as possible, on inhalation – lower. It can be done sitting or standing.
-
2
Heel lift. On the exhale, lean on your heels, pull your socks towards you, on the inhale, lower your fingers.
-
3
Rolls from heel to toe. Stand up straight, rolling from heel to toe, focusing on toes when lifting.
-
four
Jump on socks, stand on the platform (at home you can use a thick book). Stand on a hill with your heels on weight. As you exhale, raise your toes as high as possible, and as you inhale, lower them. It can be done sitting or standing.
-
five
Stop kidnapping. Sit on the floor with straight legs and an emphasis on the hands. Alternately, take each foot toward and away from you.
-
6
Toe squat. Stand up straight, feet shoulder-width apart, socks turned out to the sides. Stand on your toes and sit as deep as you can without letting your heels hit the floor. Hold at the bottom point for 1-2 seconds, then rest your feet on the floor, and return to the starting position.
-
7
Walking on toes / on the outside of the foot. Run the maximum number of steps around the room. Advanced athletes can use weights.
-
8
The light jumps into place. Jump in place, jumping on your toes.
